ADA Handicap Bathroom Requirements in California

ADA bathroom requirements are federally and state-mandated rules that ensure restrooms in public and commercial buildings are accessible to people with disabilities. In California, these rules combine the 2010 ADA Standards for Accessible Design with stricter state codes under Title 24, Chapter 11B. Together, they set legally enforceable guidelines that cover everything from door width and sink clearance to grab bar placement and signage.
This guide breaks down what California-specific ADA bathroom standards require, why compliance matters, how to meet inspection requirements, and what to expect if you’re updating an existing facility. Whether you’re a property owner, builder, or facilities manager, this is what you need to know to stay compliant and avoid costly violations.
California ADA Bathroom Standards at a Glance
- California law requires compliance with both federal ADA and state Title 24 accessibility codes.
- Bathrooms must include proper floor clearance, fixture height, signage, and turning space for wheelchairs.
- Failing to comply may result in lawsuits, fines, and damage to your business’s reputation.
- Certified Access Specialists (CASp) can evaluate your facility and help ensure compliance.
- Ongoing maintenance is essential—wear and renovations can easily trigger noncompliance.
What Are The ADA Handicap Bathroom Requirements?

ADA bathroom requirements in California refer to the mandatory accessibility features required in any public or commercial restroom. These rules ensure individuals who use wheelchairs, walkers, or have other mobility or sensory impairments can safely and independently use restroom facilities.
These standards are governed by:
- 2010 ADA Standards for Accessible Design (federal)
- California Building Code Title 24, Chapter 11B (state)
While the ADA sets the minimum, Title 24 often introduces more specific and stricter requirements—especially for fixture spacing and signage.
What Design Elements Must Be ADA Compliant?
ADA regulations apply to all parts of a bathroom, from how wide the doorway is to how high the soap dispenser sits. Here’s a breakdown of what’s required:
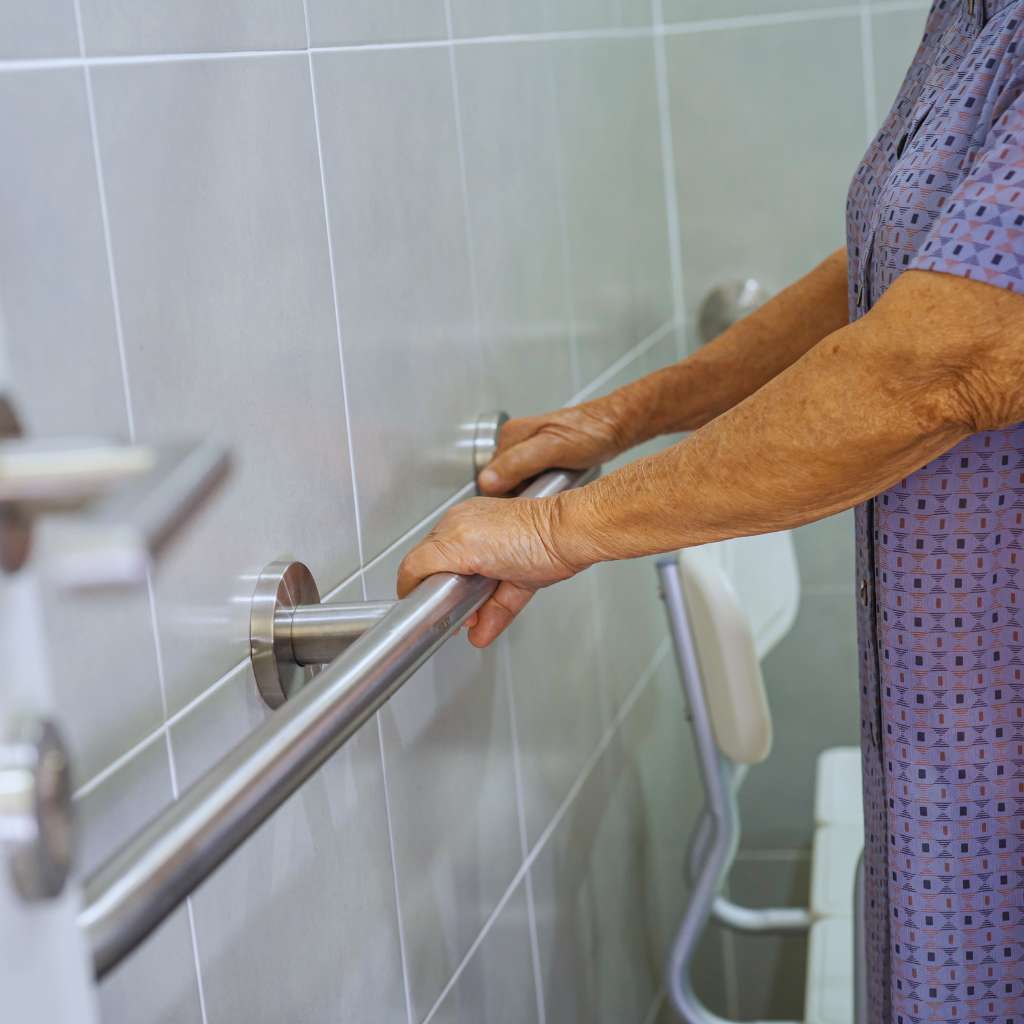
Toilet Requirements
- Seat height must be between 17 and 19 inches from the finished floor.
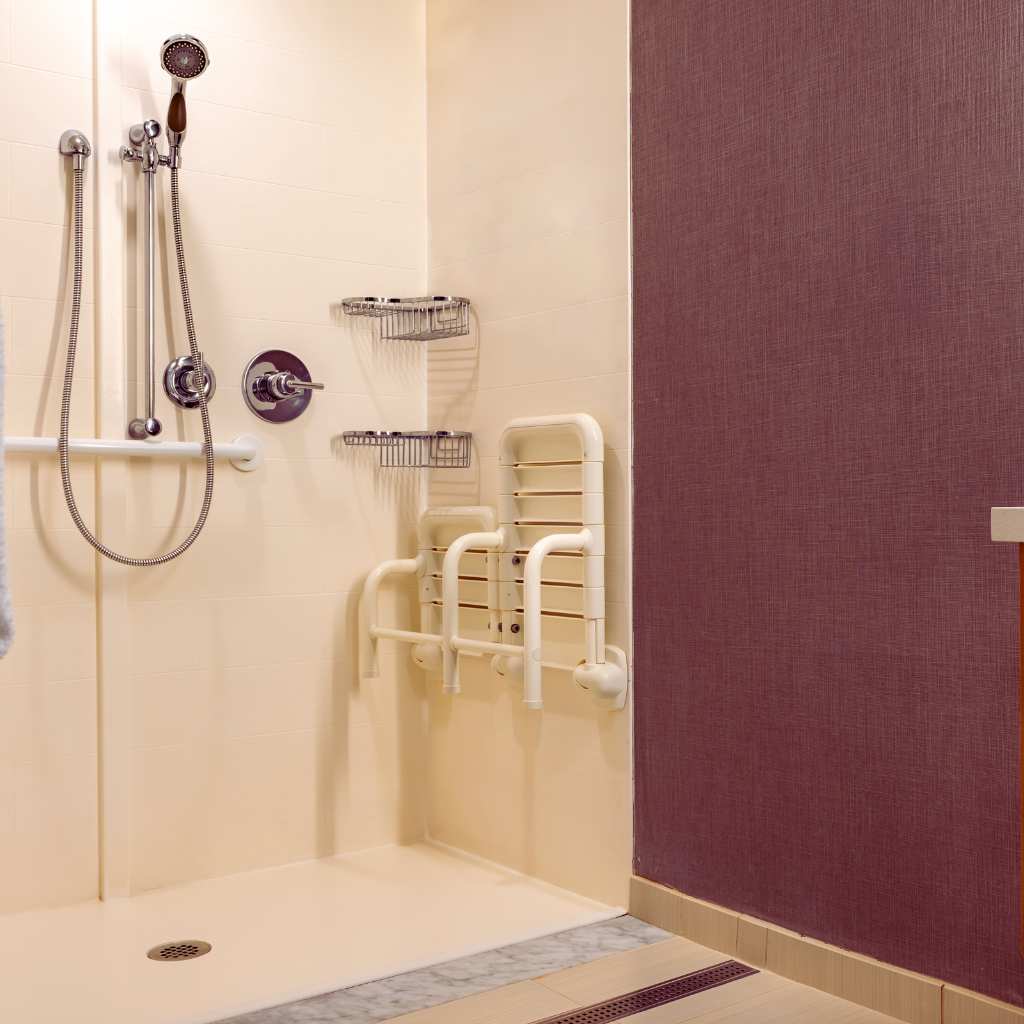
- Grab bars are required on the rear and side wall, mounted 33–36 inches high and able to support at least 250 pounds.
- Clear floor space around the toilet must be at least 60 inches wide by 56 inches deep.
- Flush controls must be operable with one hand and placed no more than 48 inches high.
Sink and Faucet Guidelines
- Sink height must not exceed 34 inches.
- Clear knee space of 27 inches minimum is required underneath for wheelchair access.
- Faucet controls must not require tight grasping—lever, push-type, or motion-activated options are acceptable.
- Exposed pipes under the sink must be insulated to avoid contact burns.
Doors and Hardware
- Minimum clear opening for doors must be 32 inches when open.
- Door hardware should be operable with a closed fist (e.g. lever handles), not knobs or tight-grip handles.
- Door swings should not obstruct fixture access.
Mirrors, Dispensers, and Accessories
- Mirrors should have a bottom edge no higher than 40 inches above the floor.
- Paper towel dispensers and soap dispensers must be reachable from a wheelchair—typically no more than 48 inches above the floor.
- Toilet paper dispensers must be 7 to 9 inches in front of the toilet and no higher than 48 inches.
Why Does ADA Compliance Matter?
ADA compliance in bathrooms is not optional—it’s a legal obligation that affects your liability, accessibility, and brand reputation.
The stakes are high:
- Legal Risk: Noncompliance opens you to lawsuits under the ADA and California’s Unruh Civil Rights Act.
- Customer Experience: Accessible restrooms serve more people and show that you take inclusion seriously.
- Reputation: Customers notice when businesses invest in accessible design.
- Insurance and Grants: Some insurers and grant programs require accessibility audits before approval.
When Is ADA Compliance Required During Renovations?
Renovations, alterations, or a change of occupancy use can trigger mandatory upgrades under both ADA and Title 24. Even minor improvements—such as installing new fixtures or retiling—can require that the entire restroom be brought into compliance. If you’re planning upgrades, our California CASp inspection services help ensure your renovation stays compliant from day one.
Disproportionate Cost Clause
If full compliance creates an excessive financial burden, California’s Title 24 includes a “disproportionate cost” rule. This allows businesses to limit upgrades to 20% of the total project cost when full compliance is not readily achievable—provided those funds are applied to the most critical access barriers first. Documentation must justify any exemption claimed.
Key triggers include:
- Alterations to existing restrooms
- Tenant improvements or remodels
- Changes in building occupancy type
The law also requires that a compliant path of travel be provided to the altered area. This includes the route from the parking area, entrance, and all public access features leading to the restroom.
Can Existing Bathrooms Be Made ADA Compliant?
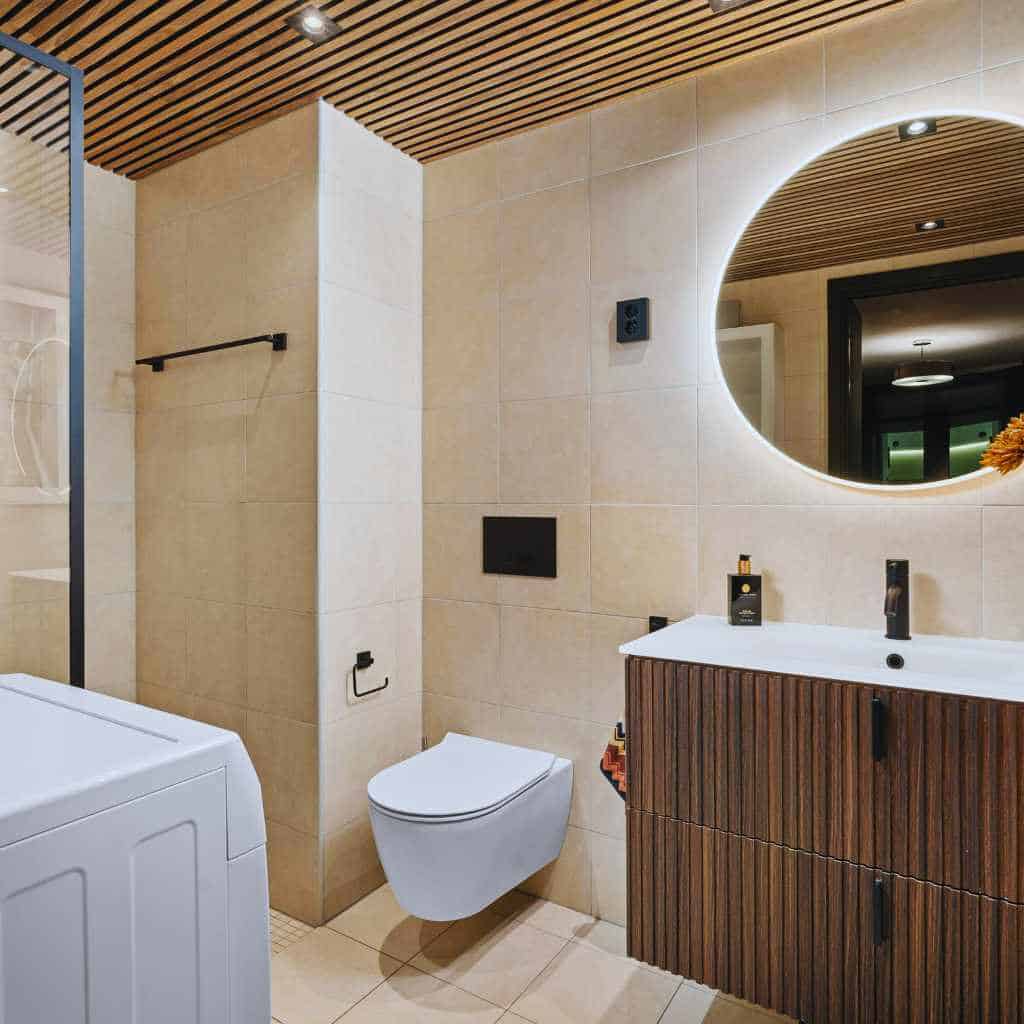

Yes, and often they must be. If your facility was built before the ADA became law—or before Title 24 updates—you may be required to retrofit certain elements to meet current accessibility standards.
Common retrofits include:
- Widening doorways and adjusting door swings
- Installing or repositioning grab bars
- Modifying sink height and providing knee clearance
- Updating signage and mirror placement
- Ensuring slip-resistant flooring
If you’re unsure where to start, our team offers CASp Compliance Consulting for Commercial Buildings in California to assess your current setup and provide a prioritized list of necessary changes.
What Are the Most Overlooked ADA Bathroom Features?
Many violations happen not from what’s missing—but from poor execution. Here’s what gets overlooked:
- Incorrect grab bar placement or inadequate anchoring
- Mirrors or dispensers too high
- Blocked floor clearance due to trash bins or storage
- Door tension or handles requiring two hands
- Fixtures installed at incorrect heights after renovations
What Are the Penalties for ADA Non-Compliance in California?
Failure to comply with accessibility laws can result in legal complaints, civil penalties, and mandatory remediation.
Key consequences include:
- Minimum statutory damages of $4,000 per violation under California’s Unruh Civil Rights Act
- Civil lawsuits from individuals or advocacy groups
- Complaints filed with the U.S. Department of Justice
Having a CASp inspection done and addressing violations within 60 days can reduce liability in some cases.
How to Prepare for an ADA Bathroom Inspection
Getting ready for a CASp inspection—or just planning an internal audit? Documentation and preparation matter.
Recommended steps:
- Review layout drawings and past permits
- Ensure fixtures meet height and clearance rules
- Provide access to all public areas and restrooms
- Keep prior CASp reports on hand for reference
A CASp will review all relevant bathroom elements under both ADA and Title 24, so being prepared improves the efficiency of the process. Our California-based CASp consultants can walk you through inspection prep and documentation support.
How Is Technology Improving ADA Bathroom Design?
New tech is making compliance easier—and better for users.
- Smart toilets with adjustable height and hands-free flushing
- Touchless faucets and soap dispensers reduce contact and improve usability
- Digital wayfinding helps users locate accessible restrooms
- Lighting automation improves visibility while conserving energy
These upgrades aren’t just about compliance—they improve safety and user experience for everyone.
PRO TIP!
Ensure ADA compliance in accessible bathrooms by maintaining a 60-inch turning radius, properly installing grab bars, and verifying that sink and toilet heights meet specifications.
Common Questions About ADA Bathroom Compliance
What is the minimum turning space in an ADA bathroom?
A minimum 60-inch diameter clear floor space is required for wheelchairs to complete a 180-degree turn.
Can older buildings be required to retrofit bathrooms?
Yes. If they are undergoing renovation or serve the public, they must be brought up to current ADA and Title 24 standards.
How high should grab bars be?
Grab bars must be mounted 33 to 36 inches above the finished floor, on both the rear and side walls near toilets.
Are all commercial restrooms required to be ADA compliant?
Yes. Almost all public-facing businesses in California must comply with ADA and Title 24 regulations.
What if my sink has no knee clearance?
You’ll need to modify it. ADA-compliant sinks must allow 27 inches of vertical clearance for wheelchairs.
Get Your Facility Assessed
If your building hasn’t had a recent CASp inspection, now’s the time. Accessibility rules change, and small violations can lead to big consequences. A proactive inspection ensures your bathrooms—and your entire facility—meet California’s strict accessibility standards.
To ensure your restrooms meet both ADA and California Title 24 requirements, explore our dedicated service for CASp Compliance Consulting for Commercial Buildings in California. Accessibility rules change, and small violations can lead to big consequences. A proactive inspection ensures your bathrooms—and your entire facility—meet California’s strict accessibility standards.
Schedule an ADA bathroom compliance inspection with a Certified Access Specialist to make sure you’re meeting both federal and state requirements.

Written by Emily Johnson
Emily Johnson is a Certified Access Specialist (CASp) Inspector and is passionate about making spaces accessible for all. With over 10 years of experience and degrees in Civil Engineering and Architecture, she inspires others while championing ADA awareness.
Get a free quote today!
By clicking “Submit”, you are signing up to receiving emails from us. You can unsubscribe whenever you like. SMS rates may apply.
Want To Know More About ADA Accessibility And How To Get Compliant?
Check out our blog!